HVAC (Heating, ventilation and air conditioning) includes all systems controlling the temperature for an enclosed area. HVAC Systems are either ducted or ductless systems. Ducted systems utilize a network of air ducts connected to a central unit. A ductless system lacks air ducts and uses other methods of air distribution.
Ducted HVAC Systems:
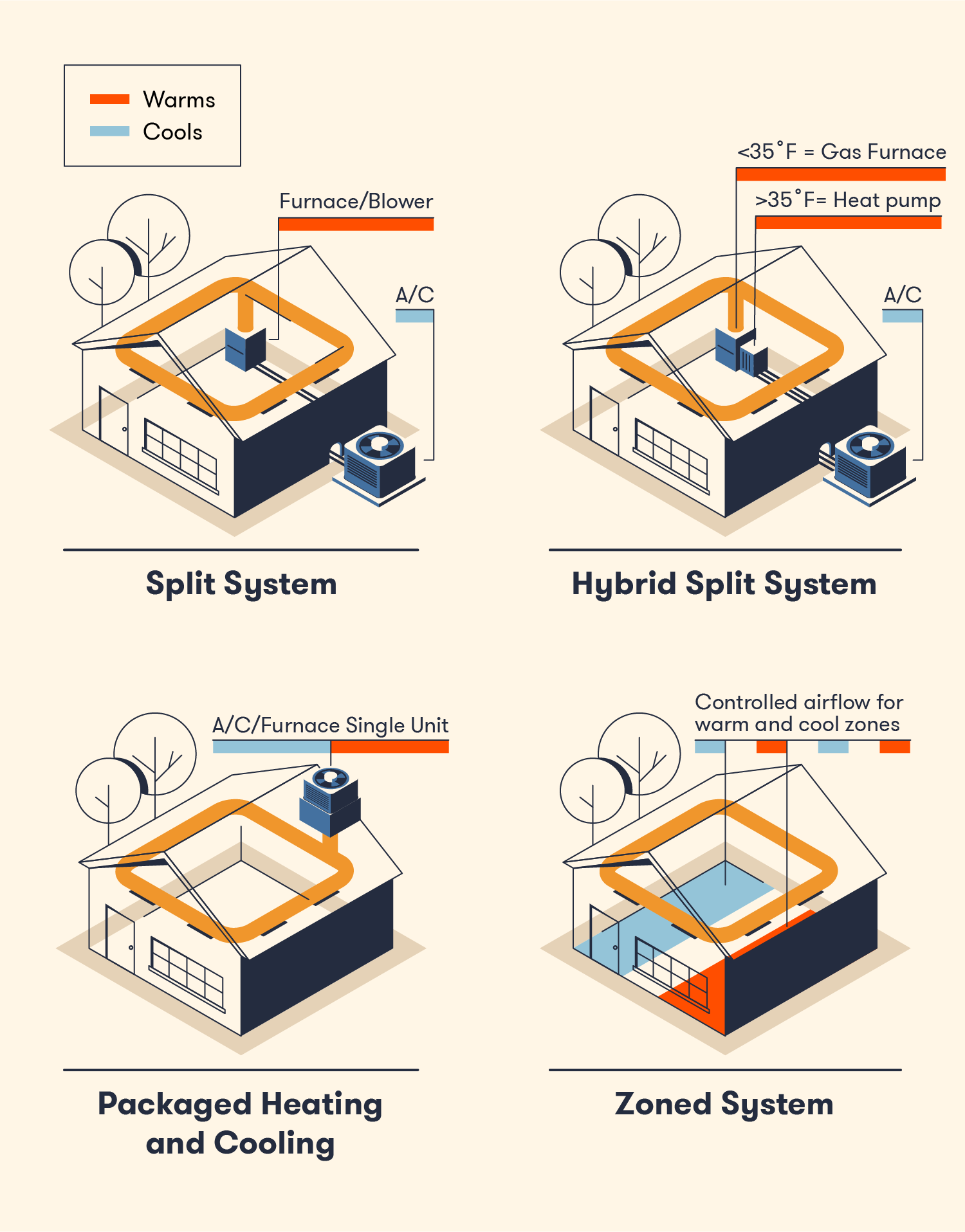
(BigRentz, 2022)
- Heating and Cooling Split System - Heating and cooling are split into separate heating and cooling components.
- Hybrid Split System - Same design as a standard Split System, but does not entirely rely on gas in order to produce heat. Electric Power can also be used that is less powerful but more efficient.
- Packaged Heating and Cooling - Cooling and Heating components are contained in a single unit that is usually stored on a roof or on the ground. Package Units are less efficient but easier to maintain and are cheaper to install than split systems.
- Zoned System - Allow greater control of the temperature across separate rooms. Manual or automatic dampers can be used to restrict the amount of airflow moving to different areas. Energy efficiency is improved by not wasting airflow on areas that do not need it.
Ductless HVAC Systems:
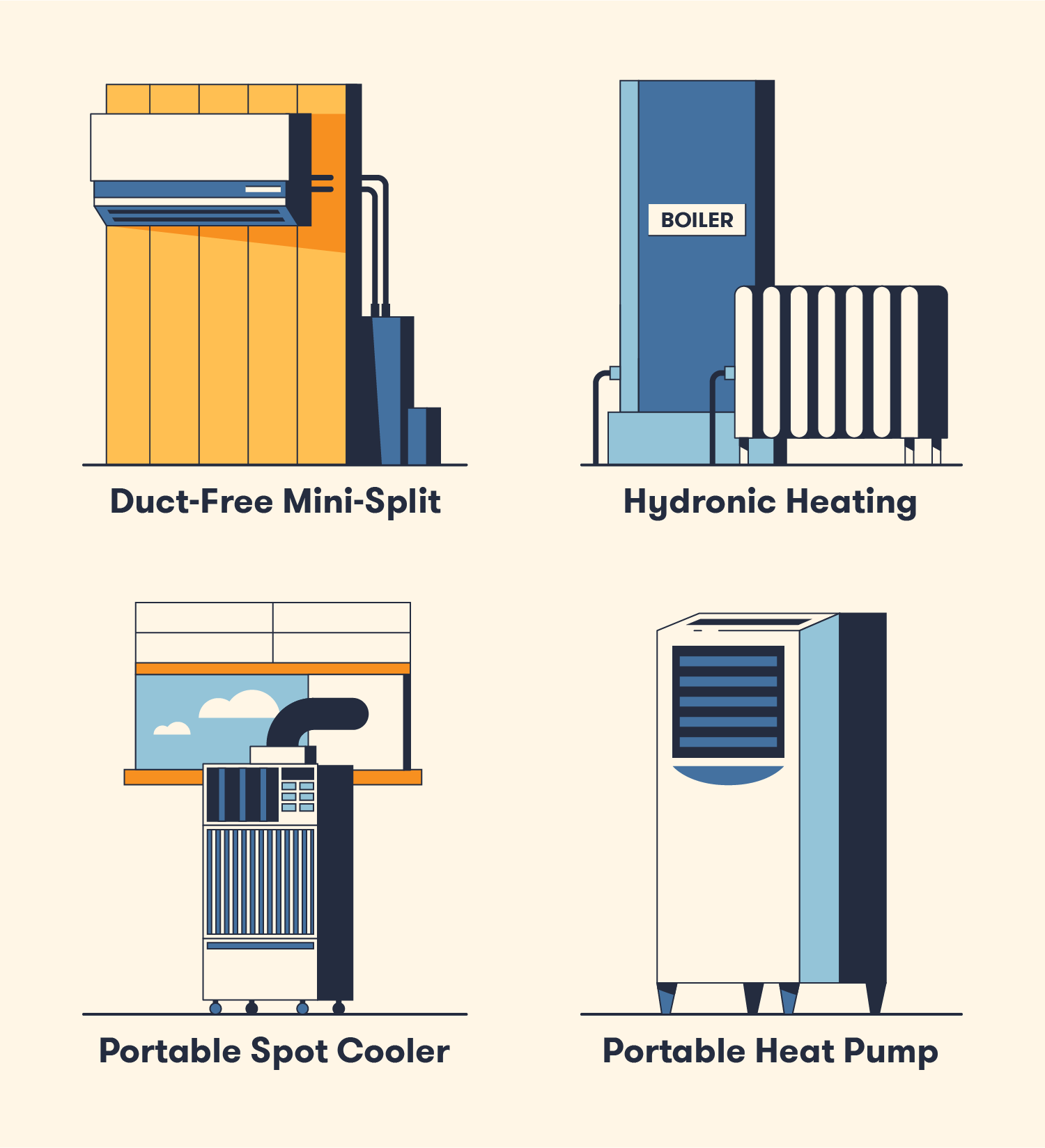
(BigRentz, 2022)
- Duct-Free Mini-Split - Often installed to regulate temperature in a single room, mini-splits use an outdoor condenser and compressor and an indoor air handler. Copper tubing connects the outside components to the inside components.
- Hydronic Heating - Uses liquid to supply heat rather than air. A boiler is used to heat water that is then distributed beneath the floors of a building through a network of pipes. Radiators utilize the heated water to heat an enclosed space.
- Portable Spot Cooler - Very easy to set up and is portable. Ambient air is cooled by refrigerant in a closed-loop coil and then pumped back out into an area. Humidity is removed from the air from the coil that is drained into a hose or tank.
- Portable Heat Pump - Similar to a spot cooler but with the addition of heating components. A heat pump is used to draw ambient air over a condenser coil that then distributes warm air around an area. Reversing the direction of the heat process with a reversing valve supplies cold air rather than hot air.
References:
BigRentz. (2022, April 21). 8 Common Types of HVAC Systems and How They Work. BigRentz. Retrieved January 4, 2023, from https://www.bigrentz.com/blog/types-of-hvac-systems
HVAC Methods and Systems:
HVAC Methods and Systems Overview
Heating and Cooling Split Systems
Michael Bernard
Comments